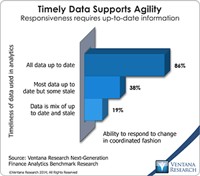
The term "corporate spend" usually refers to the incidental but still significant outlays organizations make to support operations. Especially in nonmanufacturing industries, purchases of indirect goods and business services – such as computers, office supplies, furniture and services – as well as travel and entertainment can represent a significant percentage of total costs. Technology has evolved to the point where executives – especially the chief financial officer – need to take an...
Read More
Topics:
ERP,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
digital finance
Software that automates the full scope of the accounting close, including reconciliations, consolidation and reporting, has grown more capable and affordable over the past five years. By enabling consistent process management that captures best practices, and by automating rote, repetitive activities to boost staff productivity, these applications enable organizations to shorten the close, make the process more efficient and reduce the risk of material errors by strengthening accounting...
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
ERP and Continuous Accounting,
digital finance
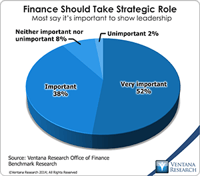
The Chief Financial Officer can enable her or his finance department play a more strategic role in company operations by adopting what I call profitability management. In the interest of time I’ve made this a very high-level description that’s intended to be just an introduction to the topic. Profitability management is a cross-functional effort. It integrates finance and sales to achieve an optimal balance of revenue and margin objectives. It’s an analytics-based approach designed achieve...
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
Continuous Planning,
CFO,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
CEO,
Integrated Business Planning
Host Analytics recently announced it will now go by the name Planful. The change formally signifies a new chapter in an evolution that began with the company’s acquisition by Vector Capital a year ago and the accession of a new CEO, Grant Halloran. Planful executives say the new name better represents its focus, which is on what Ventana Research calls continuous planning, as well as its focus on the associated processes of forecasting, analysis, consolidation and reporting.
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
Continuous Planning,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
robotic finance,
Predictive Planning
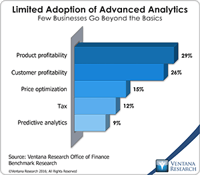
Like many other industry observers I’ve heard overblown claims for information technology for decades. However, I’ve also observed that – eventually – reality catches up with vision. Finance and accounting departments are particularly resistant to change, yet because almost no corporations use adding machines or typewriters any more, it’s clear that transformative change can happen. Nonetheless, because users of business computing systems are inundated with “it’s better than ever” promotions by...
Read More
Topics:
Social Media,
Mobile Technology,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Human Capital,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Intelligence,
Cloud Computing,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM)
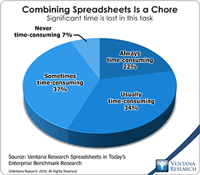
Ventana Research coined the term “enterprise spreadsheet” in 2004 to describe a variety of software applications that add a desktop spreadsheet’s user interface (usually that of Microsoft Excel) to components that address the issues that arise when desktop spreadsheets are used in repetitive, collaborative enterprise processes. Enterprise spreadsheets are designed to provide the best of both worlds in that they offer the ease of use and flexibility of desktop spreadsheets while overcoming their...
Read More
Topics:
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Intelligence,
Uncategorized,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Information Management (IM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM)
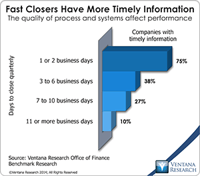
It strikes me that the motto of successful salespeople – “ABC: Always Be Closing!” – could apply equally to corporate controllers, albeit in the accounting sense. For a while now I’ve been advocating continuous accounting, a holistic approach to managing the finance and accounting function that, in part, emphasizes using technology to distribute workloads more evenly over an accounting period – in effect to always be closing rather than waiting until the end of the month or quarter. Continuous...
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM)
Vendavo is a vendor of business-to-business (B2B) price and revenue optimization software, which I have written about. A major focus of the conference sessions this year at the company’s annual user group meeting was on practical approaches to successful price optimization initiatives. While this category of software has been achieving increasing acceptance, penetration is still limited in the B2B segment, which includes, for example, industrial goods and services.
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Business Analytics,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Vendavo, price, pricing, optimization, revenue, cu
Unit4, a Netherlands-based vendor of financial management software focused mainly on midsize companies, recently acquired prevero, a German vendor of performance management and business intelligence software. The acquisition reflects a convergence of transactional and analytic business applications, which I have written about. ERP and financial management software vendors increasingly are adding analytic capabilities – especially in financial performance management (FPM) – to the core functions...
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
Business Analytics,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM)
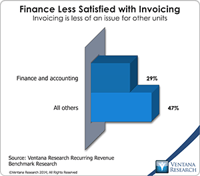
Invoicing and billing are mundane business activities that hardly anyone outside of the accounting department cares about, but they are where the back office meets the front office. How well a company handles the process of getting paid by its customers can have an impact on its relationships with them. Like most of the details of business process execution, the impact of substandard invoicing and billing is rarely obvious or even of interest to senior management. That said, like trimming scrap...
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
Cloud Computing,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM)