The use of blockchain distributed ledgers in business processes is now a common theme in many business software vendors’ presentations. The technology has a multitude of potential uses. However, presentations about the opportunities for digital transformation always leave me wondering: How is this magic going to happen? I wonder this because the details about how data flows from point A to point B via a blockchain are critically important to blockchain utility and therefore the pace of its...
Read More
Topics:
Planning,
Predictive Analytics,
Forecast,
FP&A,
Machine Learning,
Reporting,
budget,
Budgeting,
Continuous Planning,
Analytics,
Data Management,
Cognitive Computing,
Integrated Business Planning,
AI,
forecasting,
consolidating
Ventana Research uses the term “predictive finance” to describe a forward-looking, action-oriented finance organization that places emphasis on advising its company rather than fulfilling the traditional roles of a transactions processor and reporter. Technology is driving the shift away from the traditional bean-counting role. The cumulative evolution of software advances will substantially reduce finance and accounting workloads by automating most of the mechanical, rote functions in...
Read More
Topics:
Planning,
Predictive Analytics,
Forecast,
FP&A,
Machine Learning,
Reporting,
budget,
Budgeting,
Continuous Planning,
Analytics,
Data Management,
Cognitive Computing,
Integrated Business Planning,
AI,
forecasting,
consolidating
Supply and demand chain planning and execution have grown in importance over the past decade as companies have recognized that software can meaningfully enhance their competitiveness and improve their financial performance. Sales and operations planning (S&OP) is an integrated business management process first developed in the 1980s aimed at achieving better alignment and synchronization between the supply chain, production and sales functions. A properly implemented S&OP process routinely...
Read More
Topics:
Planning,
SaaS,
Sales,
Forecast,
Mobile Technology,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Human Capital,
Supply Chain Planning,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Cloud Computing,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Sales Planning,
Supply Chain,
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM),
Demand Chain,
Integrated Business Planning,
SCM Demand Planning,
S&OP
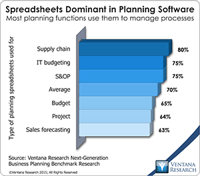
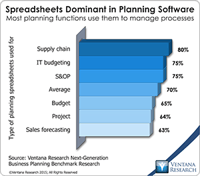
In our benchmark research at least half of participants that use spreadsheets to support a business process routinely say that these tools make it difficult for them to do their job. Yet spreadsheets continue to dominate in a range of business functions and processes. For example, our recent next-generation business planning research finds that this is the most common software used for performing 11 of the most common types of planning. At the heart of the problem is a disconnect between what...
Read More
Topics:
Planning,
ERP,
Forecast,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Reporting,
closing,
dashboard,
enterprise spreadsheet,
Excel,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Data,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Risk,
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM),
application,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management
One trend in business software that’s still in its early stages but gathering momentum is the availability of modeling tools that fill the gap between desktop spreadsheets and enterprise systems. Granted this “early stage” has been under way for quite some time, but the technology has finally progressed to the point where I expect it to get increasing market traction.
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Database,
Planning,
Forecast,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Essbase,
Quantrix,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Intelligence,
In-memory,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
finance,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Workforce Performance Management (WPM),
analysis,
analytical application,
business model,
business plan,
financial model
I believe that one of the more important analytical applications that a company can implement is profitability management. IBM Cognos offers Profitability Modeling and Optimization as part of its Cognos 10 offering that my colleague has assessed. As I’ve noted, most people in a corporation are focused on profitability, but not necessarily in a way that optimizes results across the organization in a day-to-day, consistent fashion. Those responsible for each component piece that contributes to...
Read More
Topics:
Performance Management,
Forecast,
Modeling,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
enterprise profitability management,
Business Analytics,
IBM,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Cognos,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Workforce Performance Management (WPM),
Financial Services,
Profitability
Read More
Topics:
Planning,
SAP,
Forecast,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
budget,
Budgeting,
XBRL,
Business Analytics,
Business Intelligence,
Business Mobility,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Information Management (IM),
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM),
agile,
budgeting software,
CEO,
Corporate Finance,
Financial Performance Management,
Integrated Business Planning
Alight Planning sells planning and budgeting software mainly to midsize companies and stresses its software’s ability to support a more effective approach to corporate planning and budgeting. It calls this “agile planning,” a term used to contrast a traditional, highly deterministic method of drawing up and executing plans with an “agile” mindset that is better able to deal with the high level of economic volatility that most businesses confront today. In many respects Alight’s approach is...
Read More
Topics:
Planning,
Forecast,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
budget,
Budgeting,
CFO,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM),
agile,
budgeting software,
CEO,
Integrated Business Planning