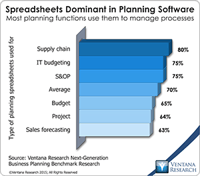
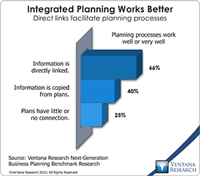
In our benchmark research at least half of participants that use spreadsheets to support a business process routinely say that these tools make it difficult for them to do their job. Yet spreadsheets continue to dominate in a range of business functions and processes. For example, our recent next-generation business planning research finds that this is the most common software used for performing 11 of the most common types of planning. At the heart of the problem is a disconnect between what...
Read More
Topics:
Planning,
ERP,
Forecast,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Reporting,
closing,
dashboard,
enterprise spreadsheet,
Excel,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Data,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Risk,
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM),
application,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management
Ventana Research recently released the results of our Next-Generation Business Planning benchmark research. Business planning encompasses all of the forward-looking activities in which companies routinely engage. The research examined 11 of the most common types of enterprise planning: capital, demand, marketing, project, sales and operations, strategic, supply chain and workforce planning, as well as sales forecasting and corporate and IT budgeting. We also aggregated the results to draw...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Planning,
Predictive Analytics,
Sales,
Social Media,
Human Capital Management,
Marketing,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Reporting,
Budgeting,
Controller,
Business Analytics,
Cloud Computing,
In-memory,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Supply Chain,
Workforce Performance Management (WPM),
capital spending,
demand management,
Financial Performance Management,
financial reporting,
FPM,
Integrated Business Planning,
S&OP
Recurring revenue is a term applied to business models that involve three types of selling and billing structures: a one-time transaction plus a periodic service charge; subscription-based services involving periodic charges; or a contractual relationship that charges periodically for goods and services. Telecommunications was the first major industry to use it, but recently the model has gained popularity in others. It is a major trend in information technology as an increasing number of...
Read More
Topics:
SaaS,
Customer Experience,
NetSuite,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Recurring Revenue,
Zuora,
Cloud Computing,
Customer Service,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
billing software,
Intacct
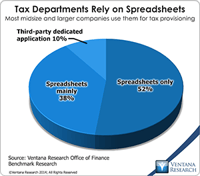
One of the issues in handling the tax function in business, especially where it involves direct (income) taxes, is the technical expertise required. At the more senior levels, practitioners must be knowledgeable about accounting and tax law. In multinational corporations, understanding differences between accounting and legal structures in various localities and their effects on tax liabilities requires more knowledge. Yet when I began to study the structures of corporate tax departments, I was...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
ERP,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
audit,
finance transformation,
LongView,
Tax,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Oracle,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Information Management (IM),
Vertex,
FPM,
Innovation Awards,
Thomson-Reuters multinational
One of the issues in handling the tax function in business, especially where it involves direct (income) taxes, is the technical expertise required. At the more senior levels, practitioners must be knowledgeable about accounting and tax law. In multinational corporations, understanding differences between accounting and legal structures in various localities and their effects on tax liabilities requires more knowledge. Yet when I began to study the structures of corporate tax departments, I was...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
ERP,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
audit,
finance transformation,
LongView,
Tax,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Oracle,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Information Management (IM),
Vertex,
FPM,
Innovation Awards,
Thomson-Reuters multinational
Business planning includes all of the forward-looking activities in which companies routinely engage. Companies do a great deal of planning. They plan sales and determine what and how they will produce products or deliver services. They plan the head count they’ll need and how to organize distribution and their supply chain. They also produce a budget, which is a financial plan. The purpose of planning is to be successful. Planning is defined as the process of creating a detailed formulation of...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Planning,
Predictive Analytics,
Marketing,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Reporting,
Budgeting,
Human Capital,
Sales and Forecasting,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Business Planning,
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Supply Chain,
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM),
Demand Planning,
Integrated Business Planning,
Project Planning,
S&OP
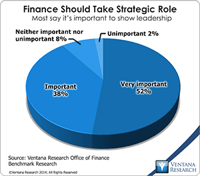
Last year Ventana Research released our Office of Finance benchmark research. One of the objectives of the project was to assess organizations’ progress in achieving “finance transformation.” This term denotes shifting the focus of CFOs and finance departments from transaction processing toward more strategic, higher-value functions. In the research nine out of 10 participants said that it’s important or very important for the department to take a more strategic role. This objective is both...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Planning,
Predictive Analytics,
Governance,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
Budgeting,
close,
end-to-end,
Tax,
Tax-Datawarehouse,
Analytics,
CIO,
In-memory,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
CPQ,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Risk,
CEO,
Financial Performance Management,
FPM
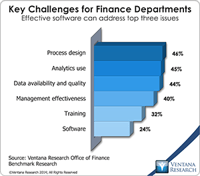
Our recently published Office of Finance benchmark research assesses a broad set of functions and capabilities of finance organizations. We asked research participants to identify the most important issues for a finance department to address in a dozen functional areas: accounting, budgeting, cost accounting, customer profitability management, external financial reporting, financial analysis, financial governance and internal audit, management accounting, product profitability management,...
Read More
Topics:
Mobile,
Planning,
Predictive Analytics,
ERP,
FP&A,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
Self-service,
Budgeting,
close,
closing,
computing,
Controller,
dashboard,
Tax,
Analytics,
Business Intelligence,
Cloud Computing,
Collaboration,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
Data,
finance,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Financial Performance Management,
FPM,
Microsoft Excel,
Spreadsheets