I recently spoke with Oversight Systems, an operational intelligence analytics company that uses predictive analytics and optimization to help companies save money, reduce the risk of loss and fraud, and reinforce corporate governance and compliance efforts. Ventana Research views operational intelligence as an emerging technology with the potential for a high return on investment. By continuously monitoring activities in a company’s IT systems, Oversight’s Web-based software continuously,...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Predictive Analytics,
Fraud,
Governance,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
audit,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Cloud Computing,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Operational Intelligence,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Information Management (IM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM),
controls,
Oversight Systems
I have commented before on the movement to adopt International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) by the United States to replace US-GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). Most recently I discussed the drive to harmonize the significant differences between US-GAAP and IFRS on revenue recognition and lease accounting. To those who are interested in but not intimately involved with the subject, I suspect the current situation is a bit confusing, since there are multiple groups...
Read More
Topics:
Reporting,
audit,
Consolidation,
IFRS,
US-GAAP accounting,
XBRL,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
Financial Management,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
financial standards,
FPM
SAP is planning to acquire e-commerce company Ariba in a transaction worth about US$4.3 billion expected to close in the third quarter of this year. Ariba provides cloud-based collaborative business commerce through a Web-based trading community that enables companies to find, connect and collaborate with a global network of partners. Its Commerce Cloud is a platform that businesses can use to buy and sell goods. Currently, Ariba counts more than 700,000 companies worldwide attached to this...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
SAP,
ERP,
EDI,
end-to-end,
Analytics,
Cloud Computing,
Uncategorized,
CRM,
SCM
I recently attended Vision 2012, IBM’s conference for users of its financial governance, risk management and performance optimization software. I reviewed the finance portion of the program in a previous blog. I’ve been commenting on governance, risk and compliance (GRC) for several years, often with the caveat that GRC is a catch-all term invented by industry analysts initially to cover a broad set of individual software applications. Each of these was designed to address specific requirements...
Read More
Topics:
Governance,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
OpenPages,
Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
IBM,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
compliance,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
controls,
IT controls
I recently attended Vision 2012, IBM’s conference for users of its financial governance, risk management and performance optimization software. From my perspective, two points are particularly worth noting with respect to the finance portion of the program. First, IBM has assembled a financial performance management suite capable of supporting core finance processes as well as more innovative ones. It continues to build out the scope of this suite’s capabilities to enhance ease of use, deepen...
Read More
Topics:
Performance Management,
close,
closing,
IFRS,
Analytics,
IBM,
Uncategorized,
GAAP
JDA Software is an established vendor of (among other categories) accounting software for the retail sector. So it is a bit ironic that the company is in the process of restating its earnings for 2008 through 2010 because of revenue recognition practices that led it to book some revenue sooner than it should have. The issue centers on certain transactions the company linked to service agreements and license revenue. As well, in 2009 and 2010 some of its license contracts included a clause...
Read More
Topics:
Performance Management,
Customer Experience,
Human Capital Management,
Office of Finance,
end-to-end,
IFRS,
JDA Software,
Business Analytics,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
GAAP
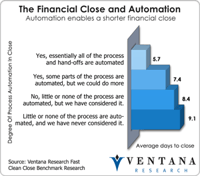
For at least a couple of decades completing the financial close within five or six business days after the end of the period has been accepted as a best practice. As such, that creates an expectation that finance organizations that take longer should work to reduce their closing intervals. In updating our last benchmark research on the closing process, Ventana Research has found this not to be the case. In fact, the latest research shows that many companies are taking longer to close today than...
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
close,
Consolidation,
Controller,
XBRL,
Business Analytics,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
CFO,
Data,
Document Management,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Information Management (IM),
Financial Performance Management
I recently attended the 2012 Global Pricing Forum hosted by Nomis Solutions, a provider of software and services to banking and finance companies. This annual event brings together thought leaders and practitioners in the area of pricing and revenue optimization (PRO). This technique uses analytics to sift through large data sets to tease out customer behavior characteristics, identify customer segments and quantify their price sensitivities. These complex calculations require software designed...
Read More
Topics:
Sales,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
credit,
financial analytics,
Nomis Solutions,
PRO,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM),
banking,
Financial Services
One of the new products that Infor announced at its recent Inforum user conference (which I covered here) is Local.ly, which is designed to facilitate localization of its applications (that is, adapting them for languages, units of measure, statutory requirements, customary processes and other specific features of the places where they will be used). Local.ly is scheduled to be released in the third quarter of this year. Infor points out that among other tasks the software can be used to...
Read More
Topics:
ERP,
Office of Finance,
Local.ly,
Tax,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Infor