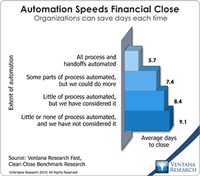
Reconciling accounts at the end of a period is one of those mundane finance department tasks that are ripe for automation. Reconciliation is the process of comparing account data (at the balance or item level) that exists either in two accounting systems or in an accounting system and somewhere else (such as in a spreadsheet or on paper). The purpose of the reconciling process is to identify things that don’t match (as they must in double-entry bookkeeping systems) and then assess the nature...
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
automation,
close,
closing,
Consolidation,
Controller,
effectiveness,
Reconciliation,
XBRL,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
Data,
Document Management,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
Financial Performance Management,
FPM
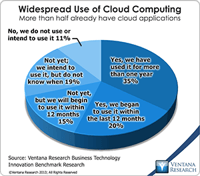
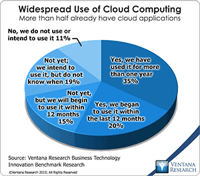
Information technologists are fond of predictions in which the next big thing quickly and entirely renders the existing thing so completely obsolete that only troglodytes would cling to such outmoded technology. While this vision of IT progress may satisfy the egos of technologists, it rarely reflects reality. Mainframes didn’t disappear, for example. Although they long ago lost their dominant position, many remain key parts of corporate computing infrastructures. The IT landscape is a hybrid...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
SaaS,
Sales,
Salesforce.com,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
PSA,
Sage Software,
Unit4,
Analytics,
Cloud Computing,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Workday,
Plex,
Professional Services Automation
Convergence is the Microsoft Dynamics business software user group’s meeting. Dynamics’ core applications are mainly in the accounting and ERP category, descendants of products Microsoft acquired: Great Plains (now GP), Solomon (SL), Navision (NAV) and Damgaard’s Axapta (AX), to which Microsoft has added its own CRM application. It has been more than a decade since the acquisitions of Great Plains (which itself had already purchased Solomon Software), and Navision, Damgaard and the software...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
SaaS,
Sales,
Salesforce.com,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Operational Performance Management (OPM),
Consulting,
distribution,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
PSA,
Sage Software,
Unit4,
Analytics,
Cloud Computing,
Business Performance Management (BPM),
CFO,
Customer Performance Management (CPM),
Financial Performance Management (FPM),
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Sales Performance Management (SPM),
Workday,
Plex,
Professional Services Automation