Ventana Research coined the term “enterprise spreadsheet” in 2004 to describe a variety of software applications that add a desktop spreadsheet’s user interface (usually that of Microsoft Excel) to components that address the issues that arise when desktop spreadsheets are used in repetitive, collaborative enterprise processes. Enterprise spreadsheets are designed to provide the best of both worlds in that they offer the ease of use and flexibility of desktop spreadsheets while overcoming their defects – chiefly inability to maintain data integrity, lack of referential integrity and dimensionality, absence of workflow and process controls, limited security and access controls as well as poor auditability. All of these issues can cause serious problems for business use, which I’ll discuss below.
Companies should investigate enterprise spreadsheet applications that can address desktop spreadsheet issues because they can provide better results, save an organization substantial amounts of time and provide greater accuracy and security. Most products are designed to be a cost-effective replacement for the desktop variety. Enterprise spreadsheets fill various roles to suit specific business needs. Some take the form of a simple data collection program that maps the spreadsheet’s two-dimensional grid to a relational or multidimensional data store. Others offer business intelligence software capabilities that enable self-service automated reporting from enterprise data sources. Still others may be relatively elaborate applications that incorporate programmed workflows, access controls, audit trails and more sophisticated visualization methods than are available in Excel and utilize a relational or multidimensional data store. Dozens of applications that incorporate enterprise spreadsheets are available today.
Enterprise spreadsheets fill an important role in corporate computing environments. For example, the spreadsheet interface has become common in business planning applications because companies find it easier to train people to use this software when it has a familiar look and feel. It might serve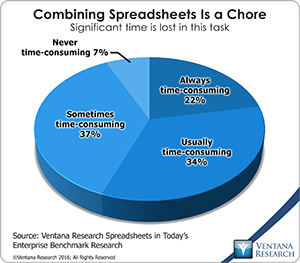 as an alternative user interface to an ERP system for specific tasks, where the object is to simplify and shorten data input or facilitate some analytical interaction (such as comparing two columns of numbers to spot matches or data inconsistencies). An enterprise spreadsheet also may serve as an automated conduit for moving data from one enterprise system to another, using macros to automate actions on the data as it moves between systems. Using macros makes it easier for business people, not IT specialists, to program these actions because far more people understand how to use them than are able to program applications or data connectors. These spreadsheets may serve as a data on-ramp or off-ramp to some process handled in an enterprise system such as ERP or CRM that requires human intervention. In this role, an enterprise spreadsheet provides the programmed workflows, security and referential integrity to fill a process gap that an enterprise system cannot address or is too expensive to implement and maintain in that core system. In addition to collecting data, enterprise spreadsheets may enrich data from an enterprise source in a controlled environment, federate data from multiple systems, perform checks or reconciliations
as an alternative user interface to an ERP system for specific tasks, where the object is to simplify and shorten data input or facilitate some analytical interaction (such as comparing two columns of numbers to spot matches or data inconsistencies). An enterprise spreadsheet also may serve as an automated conduit for moving data from one enterprise system to another, using macros to automate actions on the data as it moves between systems. Using macros makes it easier for business people, not IT specialists, to program these actions because far more people understand how to use them than are able to program applications or data connectors. These spreadsheets may serve as a data on-ramp or off-ramp to some process handled in an enterprise system such as ERP or CRM that requires human intervention. In this role, an enterprise spreadsheet provides the programmed workflows, security and referential integrity to fill a process gap that an enterprise system cannot address or is too expensive to implement and maintain in that core system. In addition to collecting data, enterprise spreadsheets may enrich data from an enterprise source in a controlled environment, federate data from multiple systems, perform checks or reconciliations 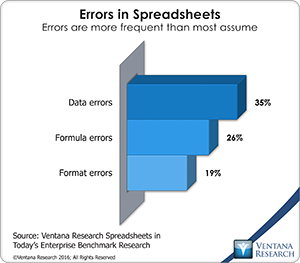 before data enters an enterprise system or perform some analysis for decision support.
before data enters an enterprise system or perform some analysis for decision support.
I regard the electronic spreadsheet as among the top five most important advances in business management to come along in the last 100 years. It revolutionized almost all aspects of running an organization. It was the original “killer app” that made it necessary for people to go out and buy a personal computer. Yet it has inherent technological defects when used in repetitive, collaborative enterprise processes. One is a lack of data integrity, which maintains the accuracy and consistency of data – spreadsheets are notoriously error-prone. More than one-third (35%) of participants in our benchmark research on spreadsheets said that data errors are common in the most important spreadsheet they use in their job, and another 26 percent said errors in formulas are common.
A related drawback is that desktop spreadsheets lack referential integrity; that is, the meaning and context of an individual cell is defined by row and column headers rather than being defined within the individual cell. This creates the familiar problem when a group of spreadsheets supposedly containing the same data are combined, but someone has added or deleted a row or column: The result is inaccurate. In our spreadsheet research more than half (56%) of spreadsheet users – even those who have been using them for more than a decade – said that they find it usually or always time-consuming to combine data from multiple spreadsheets. Another problem is that desktop spreadsheets, being two-dimensional grids, have limited ability to manipulate and report data having three or more dimensions. While accountants can work around this limit, it’s a problem for most business users because businesses work in multiple dimensions such as organizational structures (regions or divisions, for example), products (from families down to individual stock keeping units), customers (national accounts down to drop-ship locations), dimensionality and time.
They also lack programmed workflow: People attach spreadsheets to email messages, making it difficult to keep track of the latest versions. More than one-fourth (28%) of research participants said that processes that run on desktop spreadsheets frequently break down because people using them don’t know what to do next or forget to pass them along. Likewise, they lack process controls to ensure that they are reviewed properly and that any deficiencies found in the spreadsheet are noted and automatically returned to the preparer for correction. Finally, desktop spreadsheets have limited security, access controls and audit functions as well as poor auditability. To address these deficiencies, people – especially those in finance organizations – have to spend a great deal of time reviewing and correcting spreadsheets. So while our Office of Finance research finds that the accuracy of information gleaned in desktop spreadsheet processes is acceptable, fewer than one-third of organizations said that the information the finance department provides is timely.
Because enterprise spreadsheets address these issues, they can reduce the incidence of errors and malfeasance that make using spreadsheets in repetitive, collaborative enterprise processes problematic. In many cases, enterprise spreadsheets support what we call “continuous accounting” in that they ensure data quality from end to end in financial processes. Of course, not every enterprise spreadsheet product addresses all the issues I’ve mentioned. But often this doesn’t matter if, for example, the offering is designed to perform a limited set of functions such as reporting or acting as a data conduit connecting two systems in an otherwise controlled environment.
Businesses should recognize that they no longer have to put up with the shortcomings of desktop spreadsheets. They have options to have the best of both worlds, allowing people to continue working in a familiar environment but without the drawbacks that spreadsheets impose when they are used improperly. There is no good reason not to consider adopting such an application. After all, people routinely spend time exploring application options for their smartphones but rarely spend any time getting to know business software that can increase their productivity. There are many forms of enterprise spreadsheet applications to solve a range of business issues. I recommend that businesses investigate options that give users the ease, convenience and familiarity of spreadsheets without the hassle and risk that often goes with them.
Regards,
Robert Kugel
Senior Vice President Research
Follow Me on Twitter @rdkugelVR and
Connect with me on LinkedIn.












